Car filters keep impurities from breaching the parts of your car that can be harmed by debris or fumes. Maintaining these filters may not be glamorous, but it will keep your vehicle running well.
Here we look at the five filters in your car, what they filter, and the types of filters offered.
How Many Filters Does a Car Have?
- Transmission filter
- Oil filter
- Air filter
- Cabin filter
- Fuel filter
Filter types by category
-
Transmission filters
While not every car has a transmission filter, you should check your manual because if you have one, it must be changed regularly. Most vehicles with an automatic transmission have a transmission filter.
The transmission filter strains the transmission fluid to remove dirt and debris that can clog the transmission system and gunk up the moving transmission parts. A clogged filter impedes the flow of your transmission fluid, decreasing your vehicle’s performance.
Some vehicles have internal and external filters, which is a boon when filtering the transmission fluid. Unfortunately, it also doubles your chances of a clogged transmission filter.
- External Filters
Automatic cars have external filters, and some vehicles have internal and external filters. Older vehicles have external filters whose filtration space is smaller, increasing the chances of a filter clog, but are less costly than an internal filter.
They are attached to the car by a thread joint placed on the transmission housing. External filters are easier to get to, making them easy to change. They also need to be changed more often.
It is recommended to change an external filter every 30 months or every 30,000 miles, whichever comes first.
- Internal filters
Newer cars have internal filters that are more costly but have a larger filter area which lowers the chance of a clogged filter. They have a replacement requirement double their external counterpart at 55,000 to 65,000 miles.
Their location under the car and in the transmission pan makes them a bugger to change and messy too.
-
Oil filters
It’s no secret that oil is a lubricant. Its ability to cool the engine and keep moving parts lubricated to avoid wear and tear and seizing the motor to keep your engine running smoothly.
Clogged oil filters can’t stop contaminants from getting into the oil and gumming up the works. Change your oil filter when you change your oil (it makes no sense to run clean oil through a dirty filter!) every 3,000 to 5,000 miles.
New cars may have an extended period between oil changes. Check your manual to be sure!
- Full-flow oil filters
Full-flow filters are the most widely used oil filters. The oil passes through them on its way to the engine, so they filter out any dirt before it gets to the engine. They allow thickened oil to filter during winter weather while ensuring no volume loss.
- Secondary filters
This is the second filter in a car with two filters, as its name implies. It helps catch any debris missed by the full-flow filter (also called the primary filter). While they improve the life of your motor oil and offer extra protection for your vehicle, they only filter about 10% of your oil.
- Cartridge Filters
This filter is an eco-friendly version of a full-flow filter made of plastic with an inner cellulose filter. Because it is upright as opposed to lying down, it is easier to check, and no oil needs to be removed.
- Spin-on oil filters
This variation of a full-flow filter is a favorite of back alley mechanics. The ease of installation of this steel canister filter that houses a paper element requires fewer tools.
- Spinner oil filters
A spinner filter uses centrifuge-type force (created when spinning) to clarify the oil.
The barrier in the filter separates the fine particles of sediment, soot, and carbon from the oil. It is a secondary filter.
- Magnetic oil filters
This secondary magnetic filter only removes metallic pollutants from the oil. Because it is a filter that can be cleaned, it never needs replacing.
-
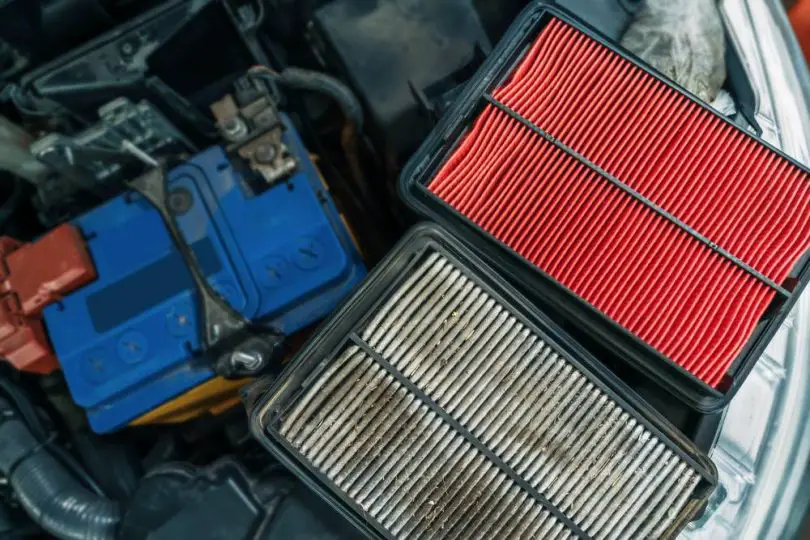
Air Filters
The air filter keeps your engine breathing. Without it, the air/fuel mixture in the engine will be off. It also ensures that dust, bugs, and any debris in the air are not sucked into the car’s engine.
Depending on the manufacturer’s recommendations, air filters should be changed between 30,000 and 50,000 miles. Living in areas with hot weather, heavy traffic, and sandy/dry soil can increase the likelihood of a clogged air filter, and they should be checked more often.
- Paper Filters
Paper filters are ideal if you live in a low dust location or own a smaller car. While they are the most popular filter due to their low cost, they are not the best choice in air filters for your vehicle.
- Gauze filters
Gauze filters offer a synthetic dry filter and an oiled filter. The synthetic filter requires periodic cleaning with synthetic filter cleaner or an equivalent.
The oiled filter, which is the most popular, requires a good cleaning about every 5,000 miles and re-oiling before reinstalling.
- Foam Filter
Lawn mowers use a foam filter, but some auto manufacturers have started covering their air filters with foam. Their cost deters most people from using them. They are best used in areas of high dust and debris.
-
Cabin Filters
When it comes to cabin filters, there is a choice of four primary options. Their unique way of filtering is what makes each stand out.
Your cabin filter keeps the inside of the car free of allergens, foul odors, and fumes from the engine. Clogged air filters can damage the A/C and heating system. Both are expensive repairs. It is worth paying the small cost for the filter to ensure the air in the car is safe to breathe.
Cabin filters should be changed every 12,000 to 15,000 miles or as the manufacturer recommends. If you live in a dry area where it is dusty or drive on unpaved back roads, you should check the cabin filter more frequently.
- Electrostatic Cabin Filters
The fibers in this filter are electrostatic in charge to draw in allergens like pollen, mildew spore, smoke, debris, dust, and fuel fumes. Thus no odors or bacteria can permeate the electrostatic filter.
- Activated carbon filters
Activated carbon filters are made of cloth or mesh with a carbon bed topped with a layer of activated charcoal. Better than a particulate filter, they filter out gaseous pollutants and smaller ones that pass a standard air filter, such as smoke and exhaust.
- Charcoal filters
These also filter better than a particulate filter because of the charcoal layer that covers the filter material. Like the activated carbon filter, charcoal filters trap exhaust fumes and smoke.
- Particulate Filters
A particulate filter is your basic cabin filter. It traps larger particles like debris, dust, and pollen while letting anything smaller than 0.3 microns, such as car exhaust and carbon monoxide, drift in.
-
Fuel Filters
A clogged fuel filter deprives your car of gas. Dirt and debris can clog your fuel injectors and starve your vehicle of gas, so the fuel pump must work harder. Changing the fuel filter between 20,000 and 60,000 miles will prevent erosion of moving engine parts.
- Primary fuel filter
The job of a primary filter is to filter large particles like asphaltenes and water. They are found in diesel engines as part of a two-filter system that includes a primary and secondary filter. It removes debris larger than 10 microns that create wear damage.
- Secondary fuel filters
A secondary fuel filter filters out the smaller contaminants that the primary filter misses. Water removal is not done by the secondary filter, whose job is to catch pollutants of less than 10 microns.
- Canister fuel filters
Cannister fuel filters are plastic or metal one-use filters with an inner filter element, like canister oil filters. They are disposable and not eco-friendly.
- Spin-on fuel filter
These are a favorite of DIYers because they can be replaced quickly and easily. This canister fuel filter can be switched out in a few minutes.
- Inline fuel filters
Attach to the car’s underbelly between the gas tank and engine. It is held in place by brackets allowing the fuel lines to enter and exit the inline filter.
- Cartridge fuel filters
Cartridge fuel filters are eco-friendly due to their removable filter that is disposable. The cartridge made of plastic or metal attaches to a mating surface and requires no changing.









Leave a Comment