The average lead/acid car battery ways approximately 40 pounds. It is the battery’s contents that give it its weight.
Since batteries are chosen by their weight, here we will look at choosing the correct weight battery for your car, how to select a battery by its weight, the types of car batteries available, and how much a car battery weighs.
Anatomy of a Car Battery: Weight Explained
**Photo Courtesy: Quora
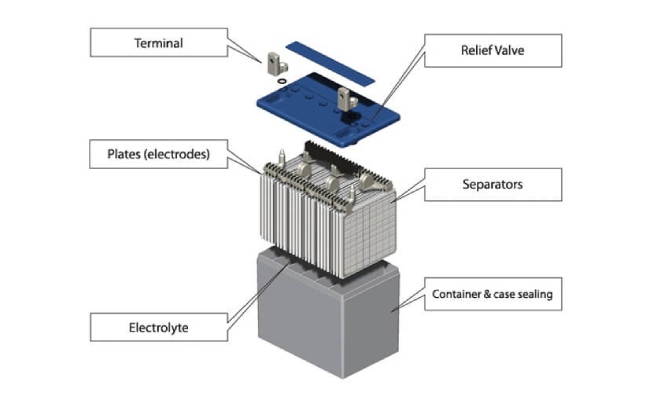
Understanding the anatomy of your car battery will help you understand why they are so hefty. All batteries have a composite plastic case that holds the battery’s cells and solutions. Different batteries have different materials that make up their cells and solution percentages.
Since batteries consisting of lead cells and acid solution are the most commonly purchased battery, here we will see what’s inside.
The plastic case is made from acid-resistant composite plastic and weighs about seven pounds. Inside the case is six lead 2.1V cells. When the battery is in use, it gives off 12.6 volts of power. Lead and lead dioxide make up these six cells separated by dividers.
These cells and their dividers sit in a bath of 65% water and 35% sulphuric acid (referred to as electrolyte solution.) The lead cells and acid solution produce a chemical reaction resulting in lead sulfate, which then reacts with the remaining plates to produce lead sulfate and hydrogen ions. The latter response generates the energy your battery uses to start and run the car’s accessories.
The lead cells and acid solution make up the battery’s weight at about 37 pounds depending on the battery. As time goes on, the solution evaporates in non-sealed batteries (batteries where a solution must be added).
In the sealed lead/acid battery (batteries where no fluid needs to be added) and non-sealed battery, continuous use weakens the acid, and eventually, the battery needs a replacement.
Importance of Battery Weight
Battery weight translates into power. Manufacturers give battery requirements by weight. Matching the weight in a new battery will provide you with the recommended power your vehicle needs.
Choosing a lower-weight battery will result in less power and poor engine performance. Most lead/acid batteries weigh approximately 38 – 42 pounds. The weight varies with the battery’s core material and solution. The length and width must also match the weight to prevent the battery from sloshing around in the tray or compartment.
Batteries come in standard weight (lead/acid batteries) and lightweight batteries weighing 20 pounds or less for compact and smaller cars like a Mini Cooper.
If you don’t know the battery weight needed for your vehicle, check your owner’s manual, the battery’s label, or you can weigh it. Remember, if you are weighing a non-sealed battery low on an acid solution, you will not get the accurate battery weight.
Not all cars have one battery. Some have two batteries, and batteries in electric vehicles are much larger than a standard car battery.
Battery Options
Electric vehicle battery
EV batteries use the same principles as acid/lead battery-positive and negative ions in an electrolyte solution to create energy.
The cells in an electric vehicle battery are made of cathode and anode terminals within separators made of light, thin insulation. The cells sit in Lithium hexafluorophosphate (LiPF6), a solution of lithium and salt. Percentages vary with the size of the EV battery.
Lithium ions move from the anode to the cathode side during recharging to generate the battery’s power. Electric vehicle batteries are some of the largest ones produced. Because of their size, they are located on the vehicle floor. They weigh around 1,000 pounds, and cars often require two batteries to drive.
Lead/Acid batteries
We covered the anatomy of these batteries earlier in the article. They come in sealed and non-sealed options. They are no-ups-no-extra batteries and make up most of the car batteries purchased.
They are popular because they are the most affordably-priced batteries, lasting three to five years. They are among the easiest batteries to install, but when installing an unsealed lead/Acid battery, take caution that it doesn’t tip so the electrolyte solution will not leak out.
Enhanced flood batteries
Enhanced flood batteries, or EFB, use cell plates with separators. They feature polyester scrim, woven fabric with a large weave that lets the sulphuric acid solution move through the cells. This helps lengthen the battery’s life. They weigh about 38 pounds which are in line with the lead/acid and AGM batteries.
Their propensity to recharge makes them an excellent choice for Automatic vehicles that do a lot of city or stop and start driving. This improved version of a lead/acid battery costs slightly more than a standard lead/acid battery.
Absorbent glass mat battery
AGM or Absorbent glass mat batteries uses boron-silicates (fiberglass sheets) between their plates to keep the 30% acid/70% water solution from spilling and creates content stabilization. They weigh about 38 pounds, depending on the size.
The boron-silicate makes the battery more movement resistant and doesn’t require an added solution making it popular with manufacturers. They are much more pricey than their lead/acid counterparts. Unfortunately, the batteries can sustain damage if left uncharged for a long time.
Gel battery
The Gel battery is literally a gel version of the lead/acid battery. The only material difference is the silica added to the acid/water solution that produces the gel-like substance. Gel batteries weigh 23 and a half pounds, 15 pounds lighter than an AGM battery and 17 pounds lighter than a lead/acid battery.
The gel increases the battery’s life and starts better with long periods between charges. One downside of the gel battery is that they require a charger that can absorb and keep track of voltage. The second downside is that they are one of the most costly batteries on the market.
How to Know When to Replace Your Battery and When to Charge It?
Ans. That will depend on the age of the battery. A battery less than two years should be recharged, but a four-year-old battery should be replaced though it may hold a charge for a while.
Checking the battery using a voltmeter will let you know the battery’s current voltage to help you make that decision.
If the battery is in the first few years of use and the weather is sweltering, it may be the weather. Recharging the battery or placing it on a trickle charger may be the answer.
If it is extreme winter weather, you may need a battery warmer after charging the battery to keep it winter-use ready.










Leave a Comment